This import format is a generic format that can be used to import features and observations data for all feature types.
Table 1 shows which data can be imported with this import type. The import type can create features that are not currently present in the domain to which the import is targeted. Existing features will not be changed in any way.
Data |
Notes |
Feature Name |
New features can be created automatically, observations for already existing features will be appended to that feature. |
Feature subtype |
Newly created features can be imported with the right feature subtype (if provided by the import file) Subtype for existing features will not be changed. If the source file contains conflicting subtypes for the same feature (in different lines) the first defined subtype will be used. |
Observation base data |
Sampling Timestamp Result timestamp Erroneous flag |
Type specific observation data |
All data for properties on level 0 of the property structure the type specific observation data |
Table 1: Data that can be imported by the generic text import type
The file format expected by generic import type is a text file structured in lines and columns. The text file can include Unicode characters encoded as UTF-8 (which is backward compatible to ANSI with codepage 65001). The file may use a BOM (Unicode byte order mark) to specify the byte order of the character encoding.
A line in the source file must be terminated by line feed character (U+000A, UTF-8: 0x0A, typical for Unix, Linux, Android, Mac OS X, BSD, and other operating systems), a carriage return (U+000D, UTF-8: 0x0D typical for Mac OS till Version 9 and other operating systems), or a carriage return immediately followed by a line feed (typical for Windows operating systems).
Leading and trailing white space characters (see table 2) will be automatically trimmed from each line. If the column separator is set to tab (U+0009) tabs will not be trimmed. The first character of a line is defined as the first non-white space character, the last character as the last not white space character.
Lines where the first character is a # (U+0023, UTF-8: 0x23) are treated as comment lines and will be ignored. If the # is contained in a line but not the first character in the line it will be treated as data. Empty lines (after trimming) except the first non-comment line after the first header line are ignored.
Each non-comment and non-empty line is separated into cells by the column separator character. The column delimiter character can be set in the import type's settings. Only one column delimiter character is allowed between two columns, i.e. for n columns you need exactly n-1 column delimiters, and column n is the column after the n-1th column delimiter.
The first two non-comment and non-empty lines are treated as header lines. Header lines contain processing information for the import. The first header line is used to define the contents of a column by specifying a column content identifier in each cell. This column content identifier is used by the Application Server to match the data in that column to some characteristic of the feature or observation. Columns with a column content identifier that is not recognized by the Application Server are ignored. The second header line is used to define the unit for numeric values if these numeric values are matched against a quantity property in the observation's type specific data property structure.
Since the column headers in header line 1 define the contents of each column, the sequence of columns is not important, however all mandatory columns need to be present. The Generic text import type defines some columns that can or must be present in every source file (see table 3). The identifiers of the properties in the type specific data property structure of the observation for the feature type that is imported are used as column content identifiers for additional feature type specific columns. See the documentation of the feature types for more information.
The data in the columns (after the header lines) can be of type numeric (and quantity), text, date & time and boolean. Table 3
|
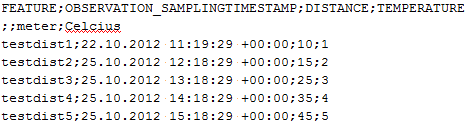
Figure 1: Example for an import source file used to import distance observations
Class |
Members |
Space Separators |
SPACE (U+0020), OGHAM SPACE MARK (U+1680), MONGOLIAN VOWEL SEPARATOR (U+180E), EN QUAD (U+2000), EM QUAD (U+2001), EN SPACE (U+2002), EM SPACE (U+2003), THREE-PER-EM SPACE (U+2004), FOUR-PER-EM SPACE (U+2005), SIX-PER-EM SPACE (U+2006), FIGURE SPACE (U+2007), PUNCTUATION SPACE (U+2008), THIN SPACE (U+2009), HAIR SPACE (U+200A), NARROW NO-BREAK SPACE (U+202F), MEDIUM MATHEMATICAL SPACE (U+205F), and IDEOGRAPHIC SPACE (U+3000) |
Line Separator |
LINE SEPARATOR character (U+2028) |
Other |
CHARACTER TABULATION (U+0009), LINE FEED (U+000A), LINE TABULATION (U+000B), FORM FEED (U+000C), CARRIAGE RETURN (U+000D), NEXT LINE (U+0085), and NO-BREAK SPACE (U+00A0). |
Table 2: White space characters
Column header identifier |
Mandatory |
|
FEATURE |
|
Name of the feature or Alias name (if an alias scheme is used) |
FEATURE_SUBTYPE |
Name of the feature subtype Default: null |
|
OBSERVATION_SAMPLINGTIMESTAMP |
|
Sampling timestamp of the observation. Must be a unique sampling timestamp. |
ERRONEOUS |
Specifies if the observation is erroneous Default: false |
Table 3: Common columns for the generic text import format
Setting |
Description |
String |
Any unicode string. The column separator is not allowed within the string. |
URI |
Any URI. The column separator is not allowed within the string. |
Quantity |
A numeric value that is read as quantity. The number must not contain grouping characters. The unit is deriver from the second header line. |
Numeric |
A numeric value that is read as quantity. The number must not contain grouping characters. |
Boolean |
A three valued Boolean value (true, false, null). The strings yes, true and 1 are interpreted as true (case insensitive), everything else is interpreted as false (except the null value string which is of course interpreted as null) |
Date time |
A date time offset value that conforms to the date time format string and date time culture given in the general import settings. |
Table 4: Supported data types with the generic import type.
Setting |
Description |
General |
|
Feature type |
The feature type for which the data shall be imported |
Null value |
The string that identifies a null value. If a cell contains a string that equals this null value string the value will be interpreted as null. If left empty empty cells will be interpreted as null. If set to a non-empty value and a cell contains an empty value this will result in an error. |
Column separator |
The column separator to be used |
Store source files |
If enabled the source files that were imported with each import session created from this import definition, will be stored on the Application Server and linked to the import session. This option gives you the possibility to store the original data files along with your import session. Default: false |
Spatial location |
|
Spatial system |
Defines the spatial system to use for features created by the import. |
Axis reference system |
Defines the axis reference system to be used for newly created features. Only used if Spatial System is set to Axis. |
Coordinate system |
Defines which coordinate system is used with newly created features. Only used if Spatial System is set to Coordinate system |
Date time format |
The format used to parse date time offset values. The Date time format is always based on the selected culture (see below). For more details on date time formats see chapter Date & time formatting |
Date time culture |
The culture used to parse date time offset values. Specifics of each of the selectable cultures can be found in the |
Table 5: Settings of the import type generic text