The data condensation: significant value change calculation type reduces the amount of observations by selecting only observations where the value of a specified parameter changed significantly in relation to the last significant observation's property value. A significant change in the parameter value is a change that exceeds a specific ε . ε can be a fixed value specified in the configuration settings or can be derived from the standard deviation.
The first observation of the source feature or calculation will always be present in the calculated feature.
Characteristic |
Description |
Supports incremental execution |
Yes |
Output typing |
Implicit by pin, derived from feature connected to input pin 1 |
Locking of source features |
Observation modification, observation deletion |
Copy |
Table 1: Calculation brief
No |
Name |
Type, Constraint |
Multiplicity (Min,Max) |
1 |
Feature to process |
Features or calculations, Feature's type must have at least one numerical or quantity property |
1,1 |
Table 2: Input pins
Configuration |
Type |
Notes |
Default value |
Include erroneous |
Boolean |
If set to true, erroneous observations of the source feature or calculation will be processed. |
False |
Inspected property |
Property |
The property that will be processed to identify which observations will be copied to the output and which observations will be skipped. |
|
Epsilon definition |
Enumeration |
Options are: •Fixed value •Derived from standard deviation |
1 |
Epsilon fixed value |
Numeric |
Effective only if Epsilon definition is set to Fixed value. |
0 |
Standard deviation fraction |
Numeric |
Effective only if Epsilon definition is set to Derived from standard deviation. |
10 |
Table 3: Configuration settings
If the calculation is the final calculation of the algorithm the used classifications of the source features or calculations has to be the used classification in the domain of the calculated feature. If this is not the case the calculation will fail.
Epsilon definition Derived ε
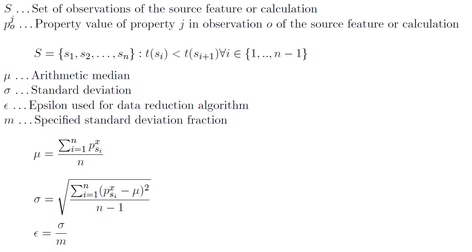
If the Epsilon definition configuration setting is set to Derived from standard deviation the ε used in the algorithm to identify significant value changes is derived from the standard deviation. See figure 1 for the formal definition of this deviation.
|
Figure 1: Deriving ε using the standard deviation and the standard deviation fraction configuration setting
Algorithm
The algorithm sequentially reads values of the specified property in all observations and checks if the difference to the last significant value is greater than ε. The first observation of a feature is always considered as significant. If the configuration setting Include last observation is true the last observation is always added to the output. See figure 2 for a formal specification of the algorithm.
|
Figure 2: The algorithm used to identify significant observations