

We say a content is assigned to a domain if it is directly linked to that domain. Content is member of a domain if it is assigned to that domain or assigned to any of the domain's parents (in case of downward propagation) or one of the subordinate domains (in case of upward propagation).
The propagation direction is either upward or downward. Upward propagation means that if a content is assigned to a domain it is member of all parent domains. Downward propagation means that if a content is assigned to a domain it is member of all subordinate domains.
Features and Sensors are propagated upward in the Domain tree. I.e. a feature or sensor assigned to a specific domain is member of all parent domains of that domain.
If in the example domain structure shown in figure 1 a feature is assigned to Domain A. 1. it is member of the Root domain, domain A, and domain A.1. It is not member of domain A.1.1, Domain A.2 or domain B.
All other data except features and sensors assigned to domains is propagated downward in the domain tree. I.e. if some data is assigned to a specific domain it is also member of all subordinate domains of that domain.
If in the example domain structure shown in figure 1 an alias scheme is assigned to domain A, the alias scheme is member of domain A, domain A.1 and domain A.1.1. It is not member of the root domain, or domain B.
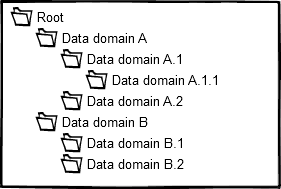
Figure 1: Example domain structure
