Identity domains are domains that enforce unique naming of Features of the same Feature type. I.e. no two Features that are member of the same identity domain and have the same feature type are allowed to have the same Feature name. The comparison of feature names in identity domains is case insensitive.
Since you might have features with the same name in different projects (e.g. the first observed house in project 1 might get the name House 01 as well as the first observed house in project 2) the system does not enforce unique naming by default. If however a domain is designated as identity domain the system enforces unique naming of all member features of the same feature type.
For defining a domain as being an identity domain the domain permission Modify (2) must be granted on that domain.
The identity domain of a specific feature is the last domain up the domain tree (including the associated domain of the feature) that is designated as identity domain.
If a non identity domain should be turned into identity domain the system will first check if all the member features (so all features assigned to this domain of any of its subordinate domains) of the same feature type are uniquely named, if not the domain cannot be turned into an identity domain.
Secondly the system will check if any domain on the path from the root domain to the domain to be changed is already an identity domain, if yes the domain cannot be turned into an identity domain.
If any of the sub domains of the domain to be changed is already an identity domain, the system will try to set those domains to non-identity domains, if it fails to do so (e.g. because of missing permissions) the domain cannot be set as an identity domain.
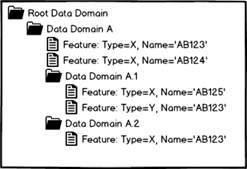
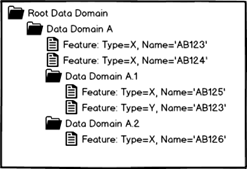
Examples: If in the structure shown in figure 1 it would not be able to set Domain A as an identity domain since there are two of type X with name AB123. In the structure shown in figure 2 Data Domain A could be set as identity domain since it has no two member having the same feature type and the same name
Figure 1: Example 1 |
Figure 2: Example 2 |