The Date-Time-Offset control is used to display and modify Date-Time-Offset values. The control consists of two elements The date-time box (Figure 1:1) allows to input or select a date and time value. The offset box (figure 1:3) is used to display and modify the offset of the date time value.
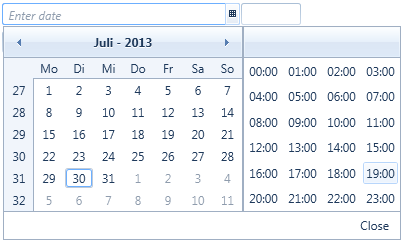
To select a date and time without actually typing the date and time value open up the picker (figure 1:2) and select the date and time value from there (figure 2). If you want to type the date time value just place focus on the date time picker and start typing. The date-time picker will parse the value as you type and will present suggestions for auto competition. To use the suggested value just press enter. Note that the date format is the format as provided by the operating system on which the Smart Client is run.
When you select a date (either by typing or by using the picker) the offset is is automatically calculated using the time zone of the Operating System on which the Smart Client is run. you can however modify the offset value manually if needed.
Typing in date and time values
The Date-Time-Offset control can parse keyed in values either in the short date time format defined by the used culture or in the military date time format derived from the short date time format of the used culture.
When keying in date time values the military time format is the most efficient way. Table 1 shows the examples of the short date time format defined by different cultures and the derived military date time format. For details about date and time format string please refer to chapter Date-time formatting.
Table 2 shows examples of date entry using military date time format (in culture German (Austria))
Culture |
Short date time format |
Military date time format |
German (Austria) |
dd.MM.yyyy hh:mm:ss |
ddMMyy hhmmss |
English (United States) |
M/d/yyyy hh:mm:ss |
MMddyy hhmmss |
English (United Kingdom) |
dd/MM/yyyy hh:mm:ss |
ddMMyy hhmmss |
Swedish (Sweden) |
yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss |
yyMMdd hhmmss |
Table 1: Date time formats used by the Date-Time-Offset controls in different cultures
Keyed in string |
Parsed date time value |
9 09 |
9th of current month, current year, at 12:00:00 |
095 0905 |
9th of May in current year, at 12:00 |
09059 090509 |
9th of May 2009 at 12:00:00 |
090509 1 090509 01 |
9th of May 2009 at 01:00:00 |
090509 015 090509 0105 |
9th of May 2009 at 01:05:00 |
090509 01053 090509 010503 |
9th of May 2009 at 01:05:03 |
0 |
Current day, current month, current year at 12:00 |
˽1 |
Current day, current month, current year at 01:00:00 |
˽01053 |
Current day, current month, current year at 01:05:03 |
Table 2: Examples for date time value entry using military format using German (Austria) as culture.
If the control is configured to allow null you can set the value of the date-time-offset to null by deleting the date. If the control does not allow null values the value will be set to the current date if deleted.
The time parts shown by the control can be different depending on the context in which the control is used, following configurations are possible
•Date only
•Date and hour
•Date, hour and minutes
•Date, hour, minutes, seconds
|
Figure 1: The date-time-offset control
|
Figure 2: The date time picker